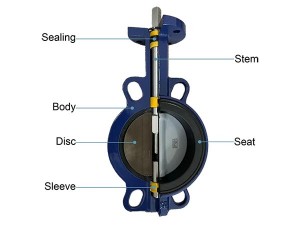
As a leading manufacturer of high-quality valves, ZFA often receives questions about the differences between various valve types. A common question is: What is the difference between a butterfly valve and a butterfly check valve? While they share similar names and both utilize a disc-type design, their functions, operations, and applications are quite different.
This guide delves into these key differences, drawing on ZFA's expertise. We'll cover the basics—such as definition, design, and operating principles. Whether you're an engineer, procurement specialist, or industry professional, this article will help you make an informed decision.
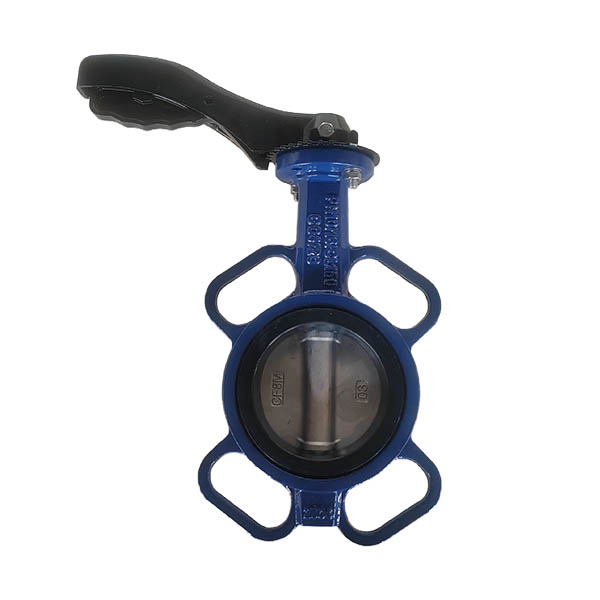
1. What is a Butterfly Valve?
A butterfly valve is a quarter-turn rotary valve primarily used for flow regulation or isolation in pipelines. It features a disc that rotates about a central axis to open or close the flow path.
1.1 How Butterfly Valve Works
The valve operates by rotating the disc 90 degrees: fully open, allowing unobstructed flow, or closed, blocking the flow path. Partial rotation allows for throttling, making it suitable for regulating flow.
1.2 Common Applications
- Water Treatment Plants
- HVAC Systems
- Chemical Processing
- Food and Beverage Industry
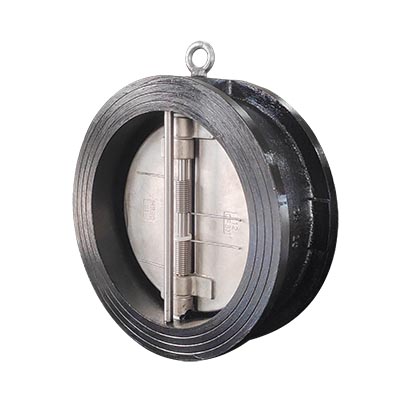
2. What is a Butterfly Check Valve?
A butterfly check valve, also known as a double-disc check valve, is a non-return valve or one way valve that prevents backflow in pipelines. Unlike butterfly valves, it operates automatically without external actuation.
2.1 Working Principle
Forward flow pushes the disc open, overcoming spring tension. When flow stops or reverses, the spring quickly closes the disc, creating a tight seal to prevent backflow. This automatic operation requires no human intervention.
2.2 Common Applications
- Pump Discharge Lines
- Compressor Systems
- Marine and Offshore Platforms
- Wastewater Management
3. Key Differences Between Butterfly Valves and Butterfly Check Valves
While both utilize a disc mechanism, their core applications are distinct. Here's a side-by-side comparison:
|
Aspect |
Butterfly Valve |
Butterfly Check Valve |
| Primary Function | Flow regulation and isolation | Backflow prevention |
| Operation | Manual or actuated rotation | Automatic (spring-loaded) |
| Disc Design | Single disc on shaft | Dual plates with hinges and springs |
| Flow Direction | Bidirectional (with proper sealing) | Unidirectional only |
| Installation | Wafer, lug, or flanged | Wafer, lug, or flanged |
This table highlights the reasons for choosing one over the other: butterfly valves for control, check valves for protection.
6. Water Hammer and Response Speed
Water hammer typically occurs when fluid flow is suddenly stopped, such as when a valve is rapidly closed or a pump is suddenly shut down. This causes kinetic energy to be converted into a pressure wave that propagates along the pipe. This shock can cause pipe bursting, flange loosening, or valve damage. Butterfly valves and butterfly check valves differ in their ability to handle water hammer due to their design and operation methods.
6.1 Butterfly Valves and Water Hammer
The speed at which a butterfly valve closes depends on its operation method (manual, pneumatic, or electric). Rapid closing can cause water hammer, especially in systems with high flow rates or high pressures. This requires special attention in pump systems.
Butterfly valves are not designed to prevent backflow. If there is a risk of backflow in the system, water hammer can be exacerbated by backflow.
6.2 Butterfly Check Valves and Water Hammer
Butterfly check valves (double-disc check valves) automatically close using spring-loaded double discs to prevent backflow. They are designed to respond quickly to changes in flow direction and ensure instantaneous closure when fluid stops or reverses, protecting the system from backflow damage. However, this rapid closure can cause water hammer.
7. FAQ
How can I quickly distinguish between a butterfly valve and a check valve?
Butterfly valves have actuators, while check valves do not.
Can a butterfly valve be used as a check valve?
No, because it lacks an automatic closing mechanism. The reverse is also true.
What maintenance do these valves require?
Butterfly valves require regular seat inspection; check valves require spring inspection every 6-12 months.